
Tunger Valb (Tokyo Electric Co., Ltd. TR-2) (Collection No.10001)
Power Supply for Early Radio
(1925-30)
-Battery, Charger, Eliminator Unit-
Battery
Early tube radio needed “A” battery for firament and “B” battery for plate.
6V Lead-acid battery similar to automobile starting battery used as “A”
.
Later, portable radio or low power consumption radio used dry cell .
“B” battery always used dry cell (22.5 – 135V)
The battery to provide negative voltage for grid bias called “C”.
Charger
Lead-acid battery eventually had to be charged.
A battery had to be taken to electric work shop or radio store and recharged at a cost.
If spere charged battery was prepared, radio wasn’t work while charging.
It is inconvenient.
If electricity provided to home, small battery charger was used.
Bibrator Charger
The contact of buzzer vibrator works as rectifier.
Using buzzer vibrator and dropper resister (always used light valve) ,you can create simple and primitive battery charger.
The output voltage is controlled by adjustable screw of contacts.
The fault of this charger is seizing contact. Continuous making contacts discharge the connected battery.
This mechanism also used as voltage regulator for automobile generator.
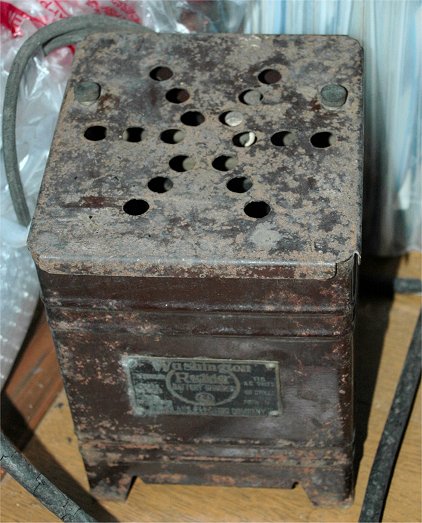
Tunger Charger
Tunger bulb is specially rectifier tube with gas for high current charging.
This rectifier was combined with dropper register to made “A” battery charger.

Tunger Valb (Tokyo Electric Co., Ltd. TR-2) (Collection No.10001)
Battery Eliminator
In late 1920’s, the power supply unit to provide “B” voltage from AC line.
It was called “battery eliminator”.
“A” battery still used or replaced charger or small transformer.
However, battery eliminator or transformer often caused “hum” trouble.

Catalogue of eliminator (U.S.A. 1920s) Left:ELRA, Right:Philco
NOTICE:
Gothic is latest updates.
Japanese terms or company
names that is untranslatable are shown in spelled in Italics.
When not mentioned specially, all prices are original retail price.
A Battery
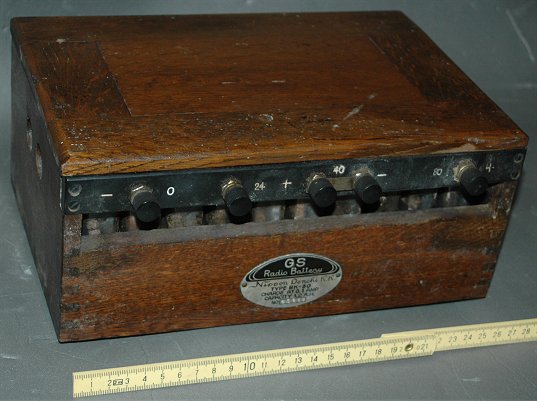
GS RADIO BATTERY Model AP-3 Nippon Denti K.K./Nihon Musen Denshin Denwa K.K. 1925?
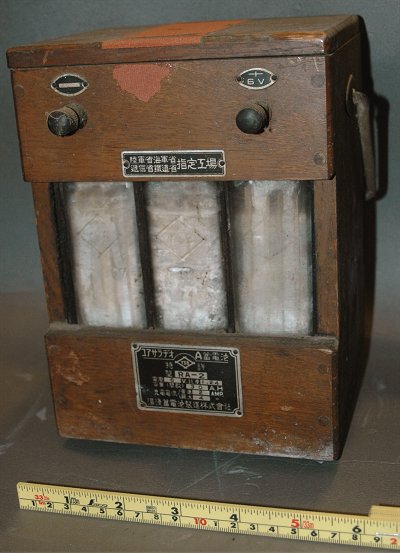
Yuasa Radio A Battery Model RA-2 Yuasa Battery MFG. Co., Ltd. 1930?
EVEREADY No.6 IGNITOR DRY CELL National Carbon Co.,Inc,(U.S.A) 1925
B battery
EVERREADY No.768 Radio "B" or "C" Battery Union Carbide and Carbon Coop. (U.S.A) 1925
GS RADIO BATTERY Model BK-80 Nippon Denti K.K. 1929
GS RADIO BATTERY Model BK-96 Nippon Denti K.K. 1929?
C Battery
Charger
Charger with Tirrill Rectifier
U.Y. Charger U.Y. Seisakusho 1929? Made in Japan
J.O. Charger J.O. Charger Seisakusho,Selling Agent: Eidensha 1929? Made in Japan
Anzen Type E No.2 Anzen Electric Co. 1931 Made in
Japan (NEW)
Charger with Tunger bulb
G.E. Tungar Charger CAT.277153 General Electric Co., U.S.A. 1925?
IDEAL Tunger Charger B A/B Tunger Charger The Ideal Electric Work 1929? Made
in Japan
TEC Tunger Charger Tokyo Electric Co., Ltd. 1928? Made in
Japan
Washington Rectifier A/B Tunger Charger High Class Electric Comany 1928? Made
in Japan
Measuring Equipent
J.T. The High Class Pocket Meter unknown 1924-26?
Battery Eliminator
RCA Duo Rectron Battery Eliminator (AP-937) Radio Corpolation of America (U.S.A) 1925-27 $65.00
Atwater Kent Model Y Power Supply Atwater Kent Manufacturing Co. (U.S.A. 1927)
Philco Radio AB Socket Power type AB356 Philaderphia Storage Battery Co.(U.S.A 1928) (NEW)
USL Model RB-135 Socket B Power U-S-L Radio, Inc., (U.S.A. 1929?)
GS RADIO BATTERY AP-3型 Nippon Denti K.K./Nihon Musen Denshin Denwa K.K. 1925?


4V lead-acid battery for German radio tube.
The nameplate of Nihon Musen Denwa K.K.(Now JRC) which was authorized dealer
of Telefunken AG was fitted.
One of cap was missing. This battery is dried up.
(Collection No.10047)
Yuasa Radio A Battery Model RA-2 Yuasa Battery MFG. Co., Ltd. 1930?



Typical 6V lead-acid battery for "A".
These battery was supplyed until 1940's for emergency battery operated
radio.
One of cap was missing. This battery is dried up.
(Collection No.10041)
EVEREADY No.6 IGNITOR DRY CELL National Carbon Co.,Inc,(U.S.A) 1925

Evereadys ignitor dry cell. It was used for low power consumption set.
(Left) B Lead-Acid Battery (Kawamatsu whole sell Catalogue 11/1937) (Right) B Dry Cell (Yasunaga whole sell Catalogue 11/1936)
45V battery with 22.5V tap was used for "B" battery.
Dry cell always used. "B" Lead-acid battery was unusual.
GS RADIO BATTERY Model BK-80 Nippon Denti K.K. 1929


This was Japanese lead-acid battery for radio “B” power.
Voltage was 80V with 40V and 24V taps. Capacity was 1.2Ah.
Cells were separable to two 40V batteries with removing short bar on the terminal.
B battery needed small current and long life.
Lead-acid battery was expensive and difficult to maintain. It was usually used dry cell.
However, in the country area, It was difficult to get the B dry cell.
Lead-acid B battery was often used in the country area.
This example was attachment of Japanese neutrodyne radio used in Nagano pref.
(Collection No.11825、consigned stuff))
GS RADIO BATTERY Model BK-96 Nippon Denti K.K. 1929?



This was Japanese lead-acid battery for radio “B” power.
Voltage was 96V with 72V, 48V and 24V taps. Capacity was 1Ah.
Cells were separable to two 48V batteries with removing short bar on the terminal.
B battery needed small current and long life.
Lead-acid battery was expensive and difficult to maintain. It was usually used dry cell.
However, in the country area, It was difficult to get the B dry cell.
Lead-acid B battery was often used in the country area.
The caps of each cells were missing. Wooden housing was corroded by acid.
(Collection No.10056)
EVERREADY No.768 Radio "B" or "C" Battery Union Carbide and Carbon Coop. (U.S.A) 1925


Eveready's "B" or "C" dry cell. This battery may be
used as "B" or "C" battery, but it can be used for
both purposes at the same time.
The voltage as "B" battery is -B, +6, +18, +19, +22.5V. The voltage
as "C" battery is 0, -3, -4.5, -16.5, -22.5V
(Collection No.11812)


Left: Made in U.S.A. (Eveready and Bergess) Right: Made in Japan (Asahi Dry cell and Komori Battery Co.)
To provide a “C” voltage, 4.5V dry cell was used.
The dry cell had some tap to provide various voltages(1.5 or 3V).
“C” battery lasted for a year.
Charger
U.Y. Charger U.Y. Seisakusho 1929?

Typical bibrator charger using two carbon electric bulb as dropper resister.
Patent No. : 85070
(Collection No.10029)
J.O.Charger J.O. Charger Seisakusho,Selling Agent: Eidensha 1929?

Typical bibrator charger using two carbon electric bulb as dropper resister.
Fitted bulb is a replica of Edison bulb. Top cover missing.
(Collection No.10024)
Anzen Type E No.2 Anzen Electric Co. 1931

This is one of the latest model of Japanese battery charger for radio.
This model was suitable for A and B battery.A small light bulb was fitted as a protection
device.
According to the instruction manual, battery must be connected before connecting to AC mains.
To prevent discharge the battery, before connecting to the AC mains, when
the battery was connected, turn the adjust screw to the small light bulb
turned off.
(Collection No.10063)
G.E. Tungar Charger CAT.277153 General Electric Co., U.S.A. 1925?




General Electric’s battery charger using “Tungar bulb” as rectifier.
This battery charger equipped small transformer and additional light bulb
socket for dropper.
It could charge various batteries from 2V to 96V.
Output capacity is 6V 2A (for “A”) or 96V 0.25A (for “B”).
This stuff was equipped Japanese Tungar bulb made by TEC.
It seemed this charger originally imported and used in Japan.
(Collection No.10054)
IDEAL Tunger Charger B The Ideal Electric Work 1929? Made in Japan
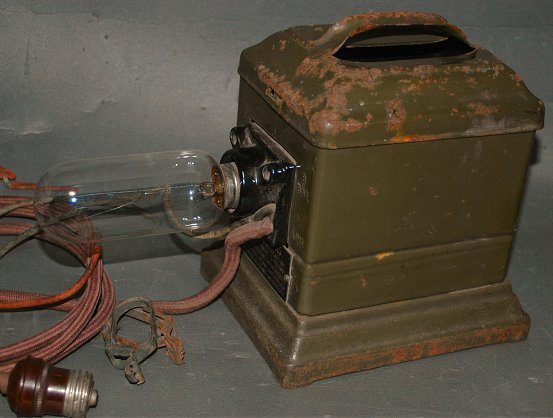
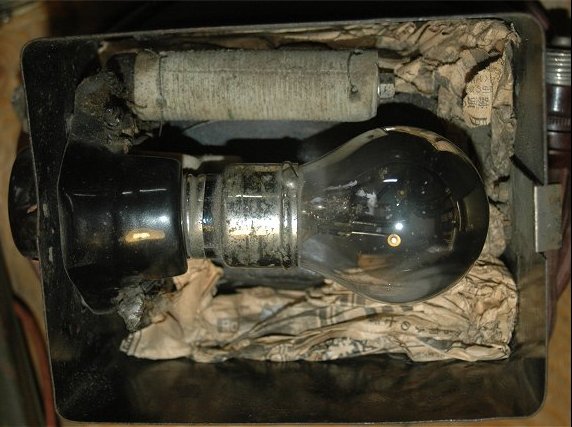




This battery charger was Japanese imitation of G.E. Tunger Carger.
Design and specification was similar to original except primary voltage (100V).
However, Quality of power transformer was poor.
(Collection No.10055)
TEC Tunger Charger Tokyo Electric Co., Ltd. 1928? Made in Japan
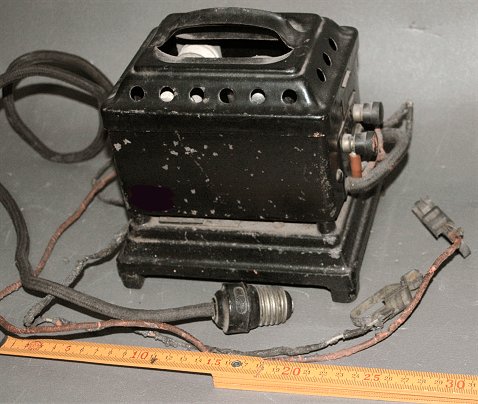
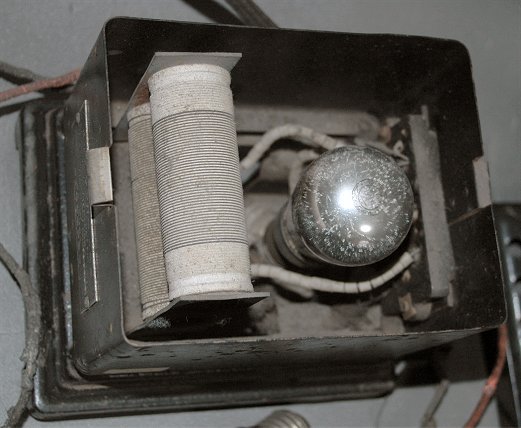



Japanese Tunger charger for "A" battery.Tokyo Electric (TEC)
was licensed from General Electric Co.,.
Shape and construction was equal to G.E. 's one (different from above model).
TEC TR-2 Tunger bulb was used.
(Collection No.10001)
Washington Rectifier A/B Tunger Charger High Class Electric Comany 1928? Made in Japan



This battery charger equipped small transformer and light bulb for dropper.
It could charge various battery from 2V to 96V. Rectifier was Tunger bulb.
This is imitation of Westinghouse chager.
(Collection No.10042)
Measuring Equipment
J.T. The High Class Pocket Meter mfr: Tajiri Seisakusho Made in Japan 1924-26?


Portable voltmeter to check battery voltage. It had 12 and 120V range.
(Collection No.10002)
Battery Eliminator
RCA Duo Rectron Battery Eliminator (AP-937) Radio Corpolation of America (U.S.A) 1925-27 $65.00


RCA Duo Rectron was designed to provide “B” voltage of DC22.5/45/90/135V 10-20mA.
It used a UX-213 full wave rectifier and X-874 voltage regulator tube.
One of terminal knob was missing.
(Collection No.10052)
Atwater Kent Model Y Power Supply Atwater Kent Manufacturing Co. (U.S.A. 1927)

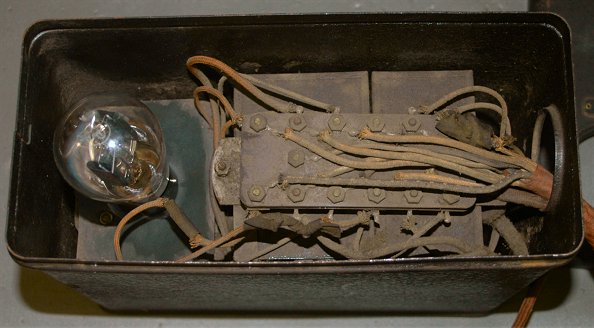


This is power pack for electric radio.
Full-wave rectifier tube 280 was used.
The model Y power pack was designed for AC tubes.
Kent’s first AC set was model 36 which was electrified model 33 with this model Y separate power pack.
(Collection No.11815)
Philco Radio AB Socket Power type AB356 Philaderphia Storage Battery Co.(U.S.A 1928)
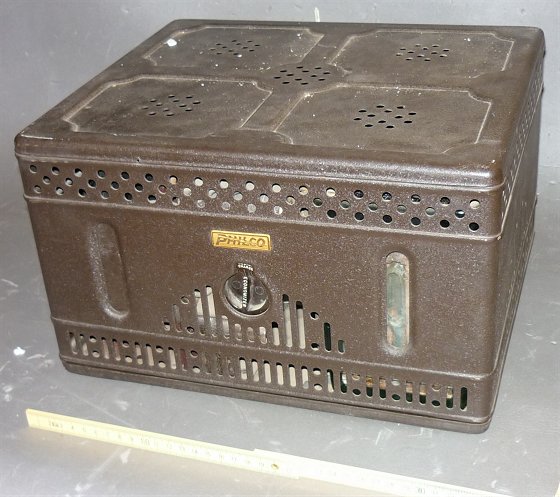
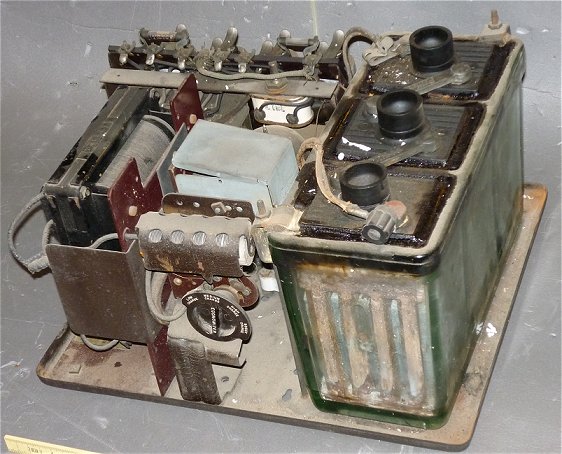




Electrolytic Rectifier: Philcotron TK-357, Input: AC110V 50/60c/s
This is battery eliminator for and B by Philco.
It had large capacity suitable for console or
large cabinet set.
The “A” power used Westinghouse Rectox Trickle
Charger (DC6V 8A) and Lead acid battery.
The “B” power used four Philco TK-357 electrolytic
rectifier.
This model was built to confirm to Underwriter’s Laboratory safety specifications.
This device could supply the power to the radio set from AC mains. However, this model could not eliminate battery
completely,
(Collection No.10062)
USL Model RB-135 Socket B Power U-S-L Radio, Inc., (U.S.A. 1929?)



TUBES: B-H (Everready Raytheon)、Input: AC110V 60Hz 15W、Max. Output: DC135V 40mA
This was “B” eliminator unit made in U.S.A. used Eveready Raytheon’s Model
B-H gaseous full wave rectifying tube.
This tube used ionized helium instead of a filament.
The specification of this tube was 300V 125mA. This spec was suitable for
B or small A power supply (such as UX-199).
This power supply equipped various B voltage outputs terminal.
It was controlled fixed resisters and variable resister.
(Collection No.10057)